History Examples
Example 1
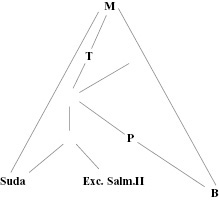
Caption
Figure 3.1 The codex Parisinus gr. 1630 (B) and the Exc.Salm.II A.
Alt Text
Roughly triangular shaped line diagram made of eight lines. The apex is labelled M and connects to the bottom right labelled B, the bottom left labelled Suda, and to an interior line labelled T. T connects to an unlabelled nexus of four lines, one of which connects to P which connects to B. T also connects via two unlabelled nexus to Suda and Exc. Salm.II in the centre bottom.
Source [Open Access]
Manafis, P. (2020). (Re)writing History in Byzantium: A Critical Study of Collections of Historical Excerpts (1st ed.). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780429351020
Example 2
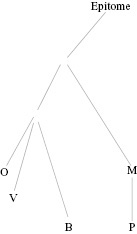
Caption
Figure 4.1 The relationship between the manuscripts of the Epitome.
Alt Text
Starting at Epitome a line connects to an undefined nexus which splits into two lines, one leading to M which then leads to P, the other leads to another undefined nexus which splits into three lines leading to O, V, and B.
Source [Open Access]
Manafis, P. (2020). (Re)writing History in Byzantium: A Critical Study of Collections of Historical Excerpts (1st ed.). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780429351020






